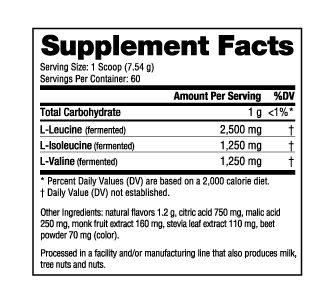
BCAA 5000 combines the powerful muscle regenerating benefits of branched chain amino acids (BCAAs). Collectively made up of leucine, isoleucine, and valine, BCAAs are known as essential amino acids because the human body cannot produce them and they must be consumed through diet or supplementation. Independently, each BCAA plays an important physiological role in the body. However, it is their synergistic combination that produces one of the most important processes involved in muscle building and recovery—muscle protein synthesis (MPS).
Top 10 reasons why BCAAs should be a part of your supplement regimen. As a whole, BCAAs support:
- Improved muscle protein synthesis
- Assist in maintaining an anabolic (muscle building) environment – Exercise can put the body in a catabolic state (muscle breakdown). When this happens, BCAAs are used for energy as opposed to growth and repair. BCAA supplementation can improve nitrogen retention by sparing other amino acid groups, which ultimately keeps the body in an anabolic state.
- Lean mass growth – BCAAs activate satellite cells that travel and attach to individual muscle fibers, helping the stressed or damaged muscle as a whole grow in size.
- Increased muscle strength – Going hand in hand with benefit #3, increases in lean mass mean large muscle fiber sizes and greater cross-sectional areas, which equates to greater increases in muscle strength.
- Improved glucose uptake and insulin sensitivity – While isoleucine improves glucose tolerance on its own, the whole trio of BCAAs can support improved insulin sensitivity and metabolic rate for improved body composition.
- Endurance performance – During prolonged exercise, BCAAs are taken up by the skeletal muscle rather than the liver in order to contribute to energy production (oxidative metabolism). They also can help prevent muscle damage during long-duration endurance sports by protecting muscle tissue
- Decreased post-exercise soreness – Also known as delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS). BCAAs help repair the muscular structural damage caused by strenuous exercise that is thought to be responsible for DOMS.
- Maintaining lean muscle mass during periods of calorie restriction – When calories are cut as a whole, this usually means a drop in protein consumption. Not enough protein and muscles may start to atrophy. Studies have shown BCAA supplementation during periods of calorie restriction can assist in maintaining lean muscle mass while also decreasing fat mass.
- Blunting muscle fatigue – Valine competes with tryptophan for entry into the brain and prevails. This means less serotonin gets to the brain, ultimately leading to stronger muscular contractions, quicker recovery between sets, and prolonged muscular strength and endurance.